A quick post on what broke after a FortiGate firmware upgrade—and the one setting that fixed it.
After upgrading a FortiGate firewall to the latest firmware, I ran into an unexpected problem:
SAML authentication suddenly stopped working for users signing in via
Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD). The configuration looked intact—certificates were present,
the SAML setup was unchanged—yet logins kept failing.
Forticlient users, will get Firewall Authentication Failed

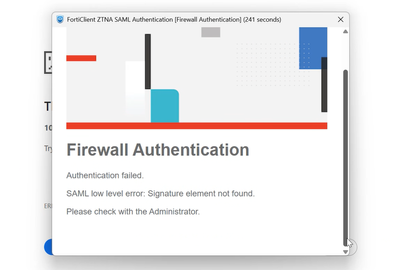
It wasn’t a lost configuration or a certificate mismatch. It turned out to be a change in
how SAML assertions are validated in the newest FortiGate versions when
Microsoft Entra ID is the Identity Provider (IdP).
The Root Cause
The latest FortiGate firmware expects the IdP to sign both the SAML response and the SAML assertion.
If your Entra ID configuration only signs the response (which used to be sufficient), authentication will fail
after the upgrade.
The Fix (Microsoft Entra ID setting)
Once this option was enabled, users were able to authenticate successfully again.
Why This Matters
Requiring signatures on both the response and the assertion strengthens the integrity of the SAML flow:
FortiGate can verify not only the envelope (response) but also the identity claims (assertion).
This improves security, but it may catch existing deployments by surprise after an upgrade.
Takeaway
- If SAML breaks after a FortiGate firmware upgrade with Entra ID as IdP, don’t assume your configuration is lost.
- Enable “Sign SAML response and assertion” in Microsoft Entra ID for the affected application.
- Re-test sign-in—authentication should start working immediately.
Reference
Fortinet community article on post-upgrade SAML issues:
Troubleshooting Tip – SAML Authentication fails after firmware upgrade
Tip: If you manage multiple FortiGate clusters, note this requirement in your upgrade checklist to avoid surprise outages.






