<#
.SYNOPSIS
This script will list all shares on a computer, and list all the share permissions for each share.
.DESCRIPTION
The script will take a list all shares on a local or remote computer.
.PARAMETER Computer
Specifies the computer or array of computers to process
.INPUTS
Get-SharePermissions accepts pipeline of computer name(s)
.OUTPUTS
Produces an array object for each share found.
.EXAMPLE
C:\PS> .\Get-SharePermissions # Operates against local computer.
.EXAMPLE
C:\PS> 'computerName' | .\Get-SharePermissions
.EXAMPLE
C:\PS> Get-Content 'computerlist.txt' | .\Get-SharePermissions | Out-File 'SharePermissions.txt'
.EXAMPLE
Get-Help .\Get-SharePermissions -Full
#>
# Written by BigTeddy November 15, 2011
# Last updated 9 September 2012
# Ver. 2.0
# Thanks to Michal Gajda for input with the ACE handling.
[cmdletbinding()]
param([Parameter(ValueFromPipeline=$True,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName=$True)]$Computer = '.')
$shares = gwmi -Class win32_share -ComputerName $computer | select -ExpandProperty Name
foreach ($share in $shares) {
$acl = $null
Write-Host $share -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host $('-' * $share.Length) -ForegroundColor Green
$objShareSec = Get-WMIObject -Class Win32_LogicalShareSecuritySetting -Filter "name='$Share'" -ComputerName $computer
try {
$SD = $objShareSec.GetSecurityDescriptor().Descriptor
foreach($ace in $SD.DACL){
$UserName = $ace.Trustee.Name
If ($ace.Trustee.Domain -ne $Null) {$UserName = "$($ace.Trustee.Domain)\$UserName"}
If ($ace.Trustee.Name -eq $Null) {$UserName = $ace.Trustee.SIDString }
[Array]$ACL += New-Object Security.AccessControl.FileSystemAccessRule($UserName, $ace.AccessMask, $ace.AceType)
} #end foreach ACE
} # end try
catch
{ Write-Host "Unable to obtain permissions for $share" }
$ACL
Write-Host $('=' * 50)
} # end foreach $share
MSSQL SP_WHO2 order by db / databases
Order sp_who2, after database with this commands:
declare @tempTable table (SPID INT,Status VARCHAR(255),
Login VARCHAR(255),HostName VARCHAR(255),
BlkBy VARCHAR(255),DBName VARCHAR(255),
Command VARCHAR(255),CPUTime INT,
DiskIO INT,LastBatch VARCHAR(255),
ProgramName VARCHAR(255),SPID2 INT,
REQUESTID INT);
INSERT INTO @tempTable
EXEC sp_who2
select *
from @tempTable order by DBName
Test SMTP TLS with OpenSSL with Auth
On a linux box type these two commands
echo -ne '[email protected]' | base64
echo -ne 'password' | base64The command will return with the username and password in base64 format.
Example:
root@Linux-homeserver:~# echo -ne '[email protected]' | base64
dXNlcm5hbWVAZG9tYWluLnByZWZpeA==
root@Linux-homeserver:~# echo -ne 'password' | base64
cGFzc3dvcmQ=So now you need to telnet with OpenSSL to the mailserver:
openssl s_client -debug -starttls smtp -crlf -connect mailserver.kennethdalbjerg.dk:465After you have connection, you need to present yourself
Example:
ehlo host.kennethdalbjerg.dkSome mailserver, do check if the ehlo is you corrert PTR record, for the IP address you are coming from, but most do not.
The mail server will return with:
250 mailserver.kennethdalbjerg.dk Hello dell1 [10.10.10.10]
You will now try to authenticated you self, if you don’t need to AUTH, please go to last code example in this blog.
AUTH LOGINAnd the mailserver will return with:
VXNlcm5hbWU6
Here you type you username in base64 format
dXNlcm5hbWVAZG9tYWluLnByZWZpeA==And the mailserver will return with:
UGFzc3dvcmQ6
Please now type you password in base64 format
cGFzc3dvcmQ=The server should now return with:
235 2.7.0 Authentication successful
After this you type normal email request to send an email
Example: (You should not type the line starting with a >, it are what the mailserver return to you.
mail from: [email protected]
> 250 2.1.0 Sender OK
rcpt to: [email protected]
> 250 2.1.5 Recipient OK
data
> 354 Start mail input; end with <CRLF>.<CRLF>
test
.
> 250 2.6.0 <604863cb-3dcc-4cee-9c1a-77fb6d951d43@mailserver.kennethdalbjerg.dk> [InternalId=9753870729240, Hostname=mailserver.kennethdalbjerg.dk] 1203 bytes in 1.581, 0,743 KB/sec Queued mail for delivery
quit
>221 2.0.0 Service closing transmission channelMatch Veeam replicas folder with VM
If you need to see what VM, that match to a VEEAM Replica folder on the disk system, this can be the solution
The veeam replica folder looks like this:
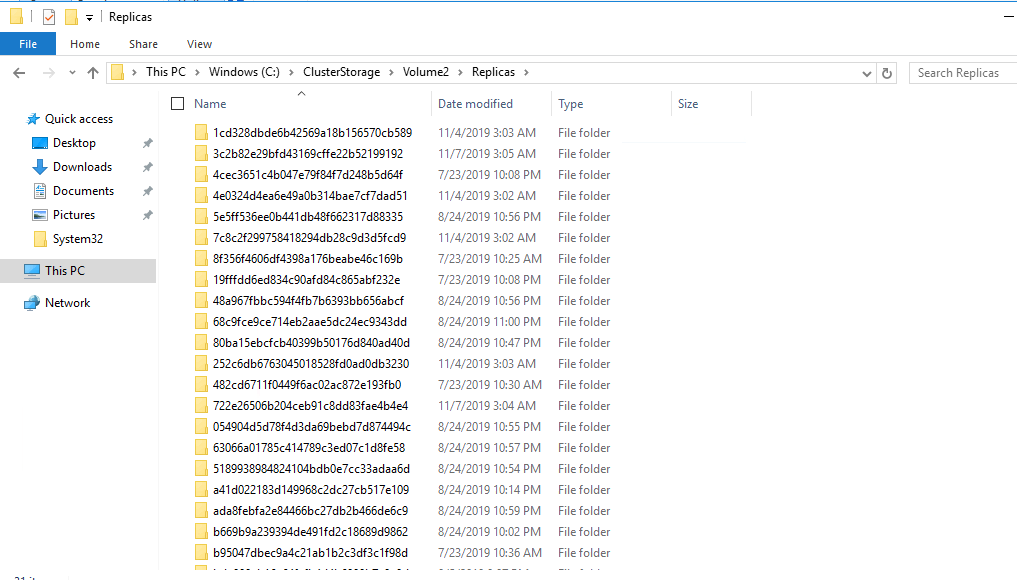
Let say that you need to find the VM, behind the folder “1cd328dbde6b42569a18b156570cb589”
Run this command on you SCVMM Powershell
get-vm | where location -like "*1cd328dbde6b42569a18b156570cb589*" | select nameThis will give you the name of the VM behind the folder “1cd328dbde6b42569a18b156570cb589”
SQL Agent Job history – T SQL
Here are a Script, that you can use to extract the SQL Agent Job History
select
j.name as 'JobName',
msdb.dbo.agent_datetime(run_date, run_time) as 'RunDateTime',
((run_duration/10000*3600 + (run_duration/100)%100*60 + run_duration%100 + 31 ) / 60)
as 'RunDurationMinutes'
From msdb.dbo.sysjobs j
INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.sysjobhistory h
ON j.job_id = h.job_id
where j.enabled = 1 --Only Enabled Jobs
--and j.name = 'TestJob' --Uncomment to search for a single job
/*
and msdb.dbo.agent_datetime(run_date, run_time)
BETWEEN '12/08/2012' and '12/10/2012' --Uncomment for date range queries
*/
order by JobName, RunDateTime descThis will also tell you the job steps
select
j.name as 'JobName',
s.step_id as 'Step',
s.step_name as 'StepName',
msdb.dbo.agent_datetime(run_date, run_time) as 'RunDateTime',
((run_duration/10000*3600 + (run_duration/100)%100*60 + run_duration%100 + 31 ) / 60)
as 'RunDurationMinutes'
From msdb.dbo.sysjobs j
INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.sysjobsteps s
ON j.job_id = s.job_id
INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.sysjobhistory h
ON s.job_id = h.job_id
AND s.step_id = h.step_id
AND h.step_id <> 0
where j.enabled = 1 --Only Enabled Jobs
--and j.name = 'TestJob' --Uncomment to search for a single job
/*
and msdb.dbo.agent_datetime(run_date, run_time)
BETWEEN '12/08/2012' and '12/10/2012' --Uncomment for date range queries
*/
order by JobName, RunDateTime descThanks to Chad Churchwell – https://www.mssqltips.com/sqlservertip/2850/querying-sql-server-agent-job-history-data/
Update Service with new SSL certificate
Some service SSL certificate is adminstrate though netsh
start netsh, though a CMD, with just type: netsh
If you then type: http show sslcert, you can see SSL certificate information:
netsh>http show sslcertSSL Certificate bindings:
-------------------------
IP:port : 0.0.0.0:443
Certificate Hash : 5f5bd1c99549b2fd7d772d32a60b8a2ba38bedd5
Application ID : {4dc3e181-e14b-4a21-b022-59fc669b0914}
Certificate Store Name : (null)
Verify Client Certificate Revocation : Enabled
Verify Revocation Using Cached Client Certificate Only : Disabled
Usage Check : Enabled
Revocation Freshness Time : 0
URL Retrieval Timeout : 0
Ctl Identifier : (null)
Ctl Store Name : (null)
DS Mapper Usage : Disabled
Negotiate Client Certificate : DisabledSo to update this ssl certificate you type:
netsh>http add sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:443 certhash=5f5bd1c99549b2fd7d772d32a60b8a2ba38bedd5 appid={4dc3e181-e14b-4a21-b022-59fc669b0914}Where 5f5bd1c99549b2fd7d772d32a60b8a2ba38bedd5 is the thumbprint of the SSL certificate. The thumbprint of a certificate can be found by running this powershell commands:
Get-ChildItem -path cert:\LocalMachine\MyLenovo Update ONECLI
OneCli.exe update acquire –scope latest –mt 7X06 –os win2016 –dir C:\Lenovo\Driver
Onecli.exe update flash –dir C:\Lenovo\Driver –scope latest
You find ONECLI on Lenovo Support page, under the specific server
Please change -mt to the machine type you are downloading for.
Restart Explorer as Adminstrator
If you have problems with accessing a drive, with the error message: f:\ is not accessible. Access is denied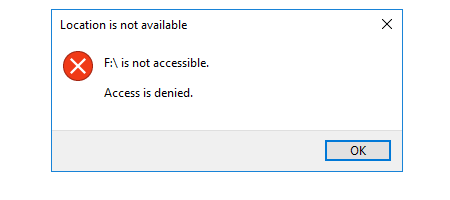
It can happen, if the drive doesn’t have this permission:
Everyone (This folder Only):
- Read & Execute
- List folder contents
- Read
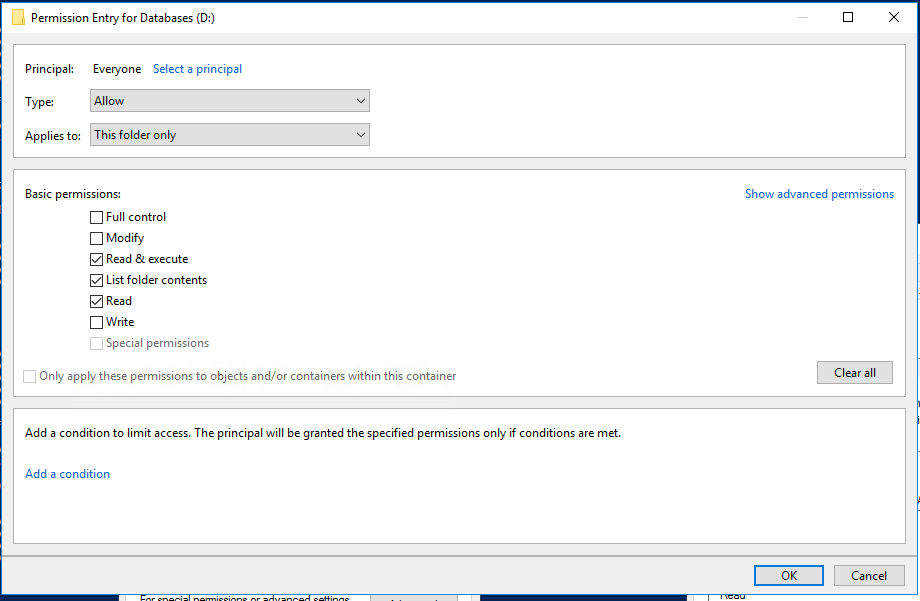
To access the drive, you need restart Explorer as administrator.
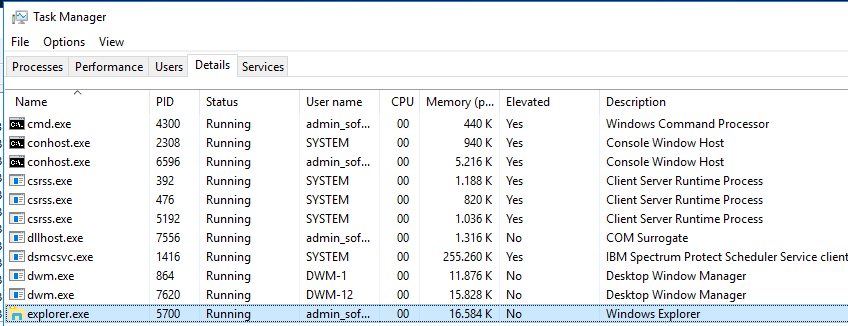
Find Explorer.exe as the user you are login as. In this example the username is admin_sofi, and kill it by right click on it and choice “End Task”
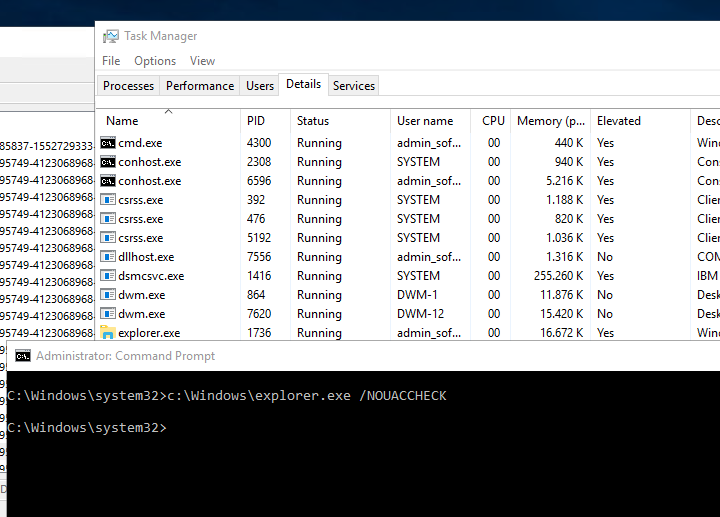
After start CMD as administrator, and write this command:
c:\windows\explorer.exe /NOACCHECK
After this you can see that explorer.exe is now running in “Elevated”
MSSQL database roles get all securables – Full script out the Database Roles
/********************************************************************
* *
* Author: John Eisbrener *
* Script Purpose: Script out Database Role Definition *
* Notes: Please report any bugs to http://www.dbaeyes.com/ *
* *
* Update: 2014-03-03 - Adjusted output to accommodate Role *
* definitions that are longer than 8000 chars *
* Update: 2013-09-03 - Added user output per Joe Spivey's comment *
* - Modified formatting for oddly named objects *
* - Included support for Grants on DMVs *
********************************************************************/
DECLARE @roleName VARCHAR(255)
SET @roleName = 'DatabaseRoleName'
-- Script out the Role
DECLARE @roleDesc VARCHAR(MAX), @crlf VARCHAR(2)
SET @crlf = CHAR(13) + CHAR(10)
SET @roleDesc = 'CREATE ROLE [' + @roleName + ']' + @crlf + 'GO' + @crlf + @crlf
SELECT @roleDesc = @roleDesc +
CASE dp.state
WHEN 'D' THEN 'DENY '
WHEN 'G' THEN 'GRANT '
WHEN 'R' THEN 'REVOKE '
WHEN 'W' THEN 'GRANT '
END +
dp.permission_name + ' ' +
CASE dp.class
WHEN 0 THEN ''
WHEN 1 THEN --table or column subset on the table
CASE WHEN dp.major_id < 0 THEN
+ 'ON [sys].[' + OBJECT_NAME(dp.major_id) + '] '
ELSE
+ 'ON [' +
(SELECT SCHEMA_NAME(schema_id) + '].[' + name FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = dp.major_id)
+ -- optionally concatenate column names
CASE WHEN MAX(dp.minor_id) > 0
THEN '] ([' + REPLACE(
(SELECT name + '], ['
FROM sys.columns
WHERE object_id = dp.major_id
AND column_id IN (SELECT minor_id
FROM sys.database_permissions
WHERE major_id = dp.major_id
AND USER_NAME(grantee_principal_id) IN (@roleName)
)
FOR XML PATH('')
) --replace final square bracket pair
+ '])', ', []', '')
ELSE ']'
END + ' '
END
WHEN 3 THEN 'ON SCHEMA::[' + SCHEMA_NAME(dp.major_id) + '] '
WHEN 4 THEN 'ON ' + (SELECT RIGHT(type_desc, 4) + '::[' + name FROM sys.database_principals WHERE principal_id = dp.major_id) + '] '
WHEN 5 THEN 'ON ASSEMBLY::[' + (SELECT name FROM sys.assemblies WHERE assembly_id = dp.major_id) + '] '
WHEN 6 THEN 'ON TYPE::[' + (SELECT name FROM sys.types WHERE user_type_id = dp.major_id) + '] '
WHEN 10 THEN 'ON XML SCHEMA COLLECTION::[' + (SELECT SCHEMA_NAME(schema_id) + '.' + name FROM sys.xml_schema_collections WHERE xml_collection_id = dp.major_id) + '] '
WHEN 15 THEN 'ON MESSAGE TYPE::[' + (SELECT name FROM sys.service_message_types WHERE message_type_id = dp.major_id) + '] '
WHEN 16 THEN 'ON CONTRACT::[' + (SELECT name FROM sys.service_contracts WHERE service_contract_id = dp.major_id) + '] '
WHEN 17 THEN 'ON SERVICE::[' + (SELECT name FROM sys.services WHERE service_id = dp.major_id) + '] '
WHEN 18 THEN 'ON REMOTE SERVICE BINDING::[' + (SELECT name FROM sys.remote_service_bindings WHERE remote_service_binding_id = dp.major_id) + '] '
WHEN 19 THEN 'ON ROUTE::[' + (SELECT name FROM sys.routes WHERE route_id = dp.major_id) + '] '
WHEN 23 THEN 'ON FULLTEXT CATALOG::[' + (SELECT name FROM sys.fulltext_catalogs WHERE fulltext_catalog_id = dp.major_id) + '] '
WHEN 24 THEN 'ON SYMMETRIC KEY::[' + (SELECT name FROM sys.symmetric_keys WHERE symmetric_key_id = dp.major_id) + '] '
WHEN 25 THEN 'ON CERTIFICATE::[' + (SELECT name FROM sys.certificates WHERE certificate_id = dp.major_id) + '] '
WHEN 26 THEN 'ON ASYMMETRIC KEY::[' + (SELECT name FROM sys.asymmetric_keys WHERE asymmetric_key_id = dp.major_id) + '] '
END COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
+ 'TO [' + @roleName + ']' +
CASE dp.state WHEN 'W' THEN ' WITH GRANT OPTION' ELSE '' END + @crlf
FROM sys.database_permissions dp
WHERE USER_NAME(dp.grantee_principal_id) IN (@roleName)
GROUP BY dp.state, dp.major_id, dp.permission_name, dp.class
SELECT @roleDesc = @roleDesc + 'GO' + @crlf + @crlf
-- Display users within Role. Code stubbed by Joe Spivey
SELECT @roleDesc = @roleDesc + 'EXECUTE sp_AddRoleMember ''' + roles.name + ''', ''' + users.name + '''' + @crlf
FROM sys.database_principals users
INNER JOIN sys.database_role_members link
ON link.member_principal_id = users.principal_id
INNER JOIN sys.database_principals roles
ON roles.principal_id = link.role_principal_id
WHERE roles.name = @roleName
-- PRINT out in blocks of up to 8000 based on last \r\n
DECLARE @printCur INT
SET @printCur = 8000
WHILE LEN(@roleDesc) > 8000
BEGIN
-- Reverse first 8000 characters and look for first lf cr (reversed crlf) as delimiter
SET @printCur = 8000 - CHARINDEX(CHAR(10) + CHAR(13), REVERSE(SUBSTRING(@roleDesc, 0, 8000)))
PRINT LEFT(@roleDesc, @printCur)
SELECT @roleDesc = RIGHT(@roleDesc, LEN(@roleDesc) - @printCur)
END
PRINT @roleDesc + 'GO'Thanks for the script to John Eisbrener – Check for new version here: https://dbaeyes.wordpress.com/2013/04/19/fully-script-out-a-mssql-database-role/
Windows 7/2008/2008 R2 Won’t boot after installation of KB4512506 / KB4512486 / KB4512476
After installation of these update, you can have problem booting you server. with this warning:
The digital signature for this file couldn’t be verified.
file:\windows\system32\winload.efi status 0xc0000428
You can fix it by booting you windows operation on the installation disc, and go to a Recovery command prompt and type these commands:
c:\> bcdedit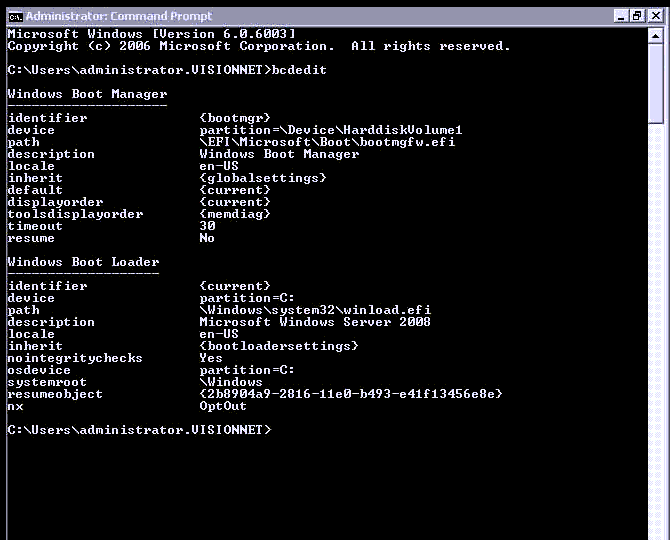
This screenshot is taken from a running Windows Server, in a recovery boot the identifier under the second Windows Boot Loader, will be named {default} instead of {current}
c:\> bcdedit -set {default} -nointegritychecks 1Replace {default} with the one from the bcdedit output.
Normal this have been resolved by installation and updated version of KB4474419, but there have not been an updated version to Windows server 2008 yet.
But to Windows 7 and Windows server 2008 R2, you can download an updated version here:
http://www.catalog.update.microsoft.com/search.aspx?q=kb4474419