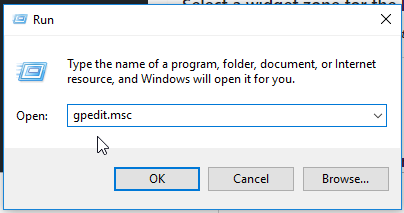
If you got an error about compression, when trying to attach the database from an enterprise version to a standard version. You will have to attach the database to an enterprise database, and remove the compression first.
The error:
sg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
RESTORE DATABASE is terminating abnormally.
Msg 909, Level 21, State 1, Line 2
Database 'abc' cannot be started in this edition of SQL Server because part or all of object 'def' is enabled with data compression or vardecimal storage format. Data compression and vardecimal storage format are only supported on SQL Server Enterprise Edition.
Msg 933, Level 21, State 1, Line 2
Database 'abc' cannot be started because some of the database functionality is not available in the current edition of SQL Server.
The SQL Command to run to disabled compression. It should be run on a query on the database with compression.
(Baware of the database will then fill something extra on the storage, so keep in mind that you need to have space available for that.)
SELECT DISTINCT 'ALTER TABLE [' + SCHEMA_NAME(schema_id) + '].[' + NAME + '] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);'
FROM sys.partitions p
join sys.objects o
on p.object_id = o.object_id
WHERE o.TYPE = 'u'
and data_compression_desc != 'NONE'
UNION
SELECT 'ALTER INDEX ALL ON [' + SCHEMA_NAME(schema_id) + '].[' + NAME + '] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);'
FROM sys.partitions p
join sys.objects o
on p.object_id = o.object_id
WHERE o.TYPE = 'u'
and data_compression_desc != 'NONE'
If the database have compression it will output with multiple SQL commands. Run these command against you database aswell
Example: (You should run what you rnu of the script output)
ALTER INDEX ALL ON [dbo].[MSSBatchHistory] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER INDEX ALL ON [dbo].[MSSChangeLogCookies] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER INDEX ALL ON [dbo].[MSSCrawlDeletedURL] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER INDEX ALL ON [dbo].[MSSCrawlDeletedURLLog] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER INDEX ALL ON [dbo].[MSSCrawlHistoryLocal] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER INDEX ALL ON [dbo].[MSSCrawlReportCrawlErrors] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER INDEX ALL ON [dbo].[MSSCrawlURL] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER INDEX ALL ON [dbo].[MSSCrawlURLLog] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER INDEX ALL ON [dbo].[MSSCrawlURLReport] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER INDEX ALL ON [dbo].[MSSDocIDsAvailable] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER INDEX ALL ON [dbo].[MSSDocIDsDeleted] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER INDEX ALL ON [dbo].[MSSNextDocID] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[MSSBatchHistory] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[MSSChangeLogCookies] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[MSSCrawlDeletedURL] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[MSSCrawlDeletedURLLog] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[MSSCrawlHistoryLocal] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[MSSCrawlReportCrawlErrors] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[MSSCrawlURL] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[MSSCrawlURLLog] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[MSSCrawlURLReport] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[MSSDocIDsAvailable] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[MSSDocIDsDeleted] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[MSSNextDocID] REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = NONE);