To list all unmanage on a nimble storage, you can ssh to the SAN, and run this command:
snap --list --unmanaged --allTo list all unmanage on a nimble storage, you can ssh to the SAN, and run this command:
snap --list --unmanaged --allI need to find a way to see if the backup chain where broken. On my search I found this could script, created by “hot2use”
I have found this script on a forum.
https://dba.stackexchange.com/questions/204883/how-to-tell-if-a-backup-log-chain-is-broken
The script is very cool, as it will tell you the backup information, from a database. All you need to do is change this ‘<DATABASENAME>’ to yours database name, example ‘MASTER’.
It will also include if a job where COPY ONLY, and where the backup is save.
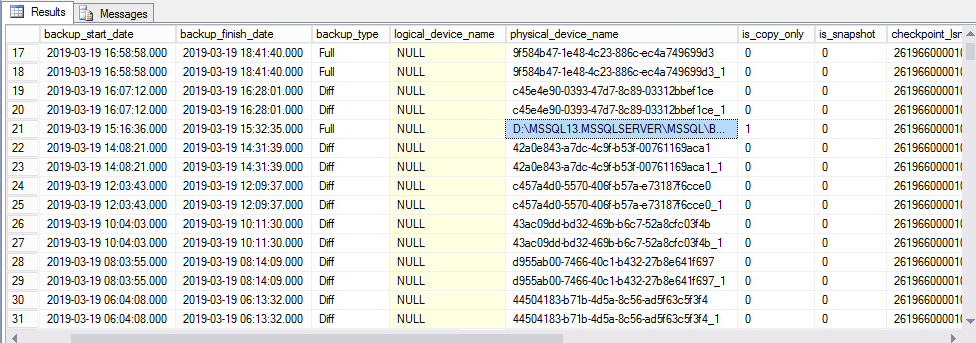
You can see in the screenshot below, that someone have run a full backup and save it on the D:\ drive, but it where a copy only so the backup is not broken.
/* ==================================================================
Author......: hot2use
Date........: 25.04.2018
Version.....: 0.1
Server......: localhost (first created for)
Database....: msdb
Owner.......: -
Table.......: various
Type........: Script
Name........: ADMIN_Retrieve_Backup_History_Information.sql
Description.: Retrieve backup history information from msdb database
............
............
............
History.....: 0.1 h2u First created
............
............
================================================================== */
SELECT /* Columns for retrieving information */
-- CONVERT(CHAR(100), SERVERPROPERTY('Servername')) AS SRVNAME,
msdb.dbo.backupset.database_name,
msdb.dbo.backupset.backup_start_date,
msdb.dbo.backupset.backup_finish_date,
-- msdb.dbo.backupset.expiration_date,
CASE msdb.dbo.backupset.type
WHEN 'D' THEN 'Full'
WHEN 'I' THEN 'Diff'
WHEN 'L' THEN 'Log'
END AS backup_type,
-- msdb.dbo.backupset.backup_size / 1024 / 1024 as [backup_size MB],
msdb.dbo.backupmediafamily.logical_device_name,
msdb.dbo.backupmediafamily.physical_device_name,
-- msdb.dbo.backupset.name AS backupset_name,
-- msdb.dbo.backupset.description,
msdb.dbo.backupset.is_copy_only,
msdb.dbo.backupset.is_snapshot,
msdb.dbo.backupset.checkpoint_lsn,
msdb.dbo.backupset.database_backup_lsn,
msdb.dbo.backupset.differential_base_lsn,
msdb.dbo.backupset.first_lsn,
msdb.dbo.backupset.fork_point_lsn,
msdb.dbo.backupset.last_lsn
FROM msdb.dbo.backupmediafamily
INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.backupset
ON msdb.dbo.backupmediafamily.media_set_id = msdb.dbo.backupset.media_set_id
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Generic WHERE statement to simplify selection of more WHEREs
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
WHERE 1 = 1
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
WHERE statement to find Device Backups with '{' and date n days back
------------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
-- AND physical_device_name LIKE '{%'
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WHERE statement to find Backups saved in standard directories, msdb.dbo.backupfile AS b
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
-- AND physical_device_name LIKE '[fF]:%' -- STANDARD F: Backup Directory
-- AND physical_device_name NOT LIKE '[nN]:%' -- STANDARD N: Backup Directory
-- AND physical_device_name NOT LIKE '{%' -- Outstanding Analysis
-- AND physical_device_name NOT LIKE '%$\Sharepoint$\%' ESCAPE '$' -- Sharepoint Backs up to Share
-- AND backupset_name NOT LIKE '%Galaxy%' -- CommVault Sympana Backup
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WHERE Statement to find backup information for a certain period of time, msdb.dbo.backupset AS b
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
AND (CONVERT(datetime, msdb.dbo.backupset.backup_start_date, 102) >= GETDATE() - 7) -- 7 days old or younger
AND (CONVERT(datetime, msdb.dbo.backupset.backup_start_date, 102) <= GETDATE()) -- n days old or older
*/
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WHERE Statement to find backup information for (a) given database(s)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
AND database_name IN ('<DATABASENAME>') -- database names
-- AND database_name IN ('rtc') -- database names
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ORDER Clause for other statements
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
--ORDER BY msdb.dbo.backupset.database_name, msdb.dbo.backupset.backup_finish_date -- order clause
---WHERE msdb..backupset.type = 'I' OR msdb..backupset.type = 'D'
ORDER BY
--2,
2 DESC,
3 DESC import-module msonline
(install-module msonline)
$O365CREDS = Get-Credential
$ONPREMCREDS = Get-Credential #used UPN Username
$SESSION = New-PSSession -ConfigurationName Microsoft.Exchange -ConnectionUri https://ps.outlook.com/powershell -Credential $O365CREDS -Authentication Basic -AllowRedirection
Import-PSSession $SESSION
Connect-MsolService -Credential $O365CREDS
#You can run these commands, to check for old MoveRequest or all mailbox in Office365, just remove the hash.
#get-moverequest
#get-mailbox
get-mailbox -id MAILBOX | New-MoveRequest -OutBound -RemoteTargetDatabase DB01 -RemoteHostName owa.domain.prefix -RemoteCredential $ONPREMCREDS -TargetDeliveryDomain ‘InternalAdDomain.prefix’
#Replace MAILBOX with the mailbox
# Replace owa.domain.prefix with the public owa address
# Replace InternalAdDomain.prefix with the internal ad domain name
#You can then run the following commands to check the mailbox moverequest status
Get-MoveRequest | Get-MoveRequestStatistics
Be aware that the user need to be an locally AD users, before you can migrated it back. It can’t be a Cloud users.
See here how to connect the user to an AD user: https://www.codetwo.com/admins-blog/how-to-merge-an-office-365-account-with-an-on-premises-ad-account-after-hybrid-configuration/
This command, can be run on both the primary and secondary node.
SELECT local_database_name
,role_desc
,internal_state_desc
,transfer_rate_bytes_per_second
,transferred_size_bytes
,database_size_bytes
,start_time_utc
,end_time_utc
,estimate_time_complete_utc
,total_disk_io_wait_time_ms
,total_network_wait_time_ms
,is_compression_enabled
FROM sys.dm_hadr_physical_seeding_statsTo see witch session id, that run command against a database, you can run this:
SELECT session_id
FROM sys.dm_exec_sessions
WHERE database_id = db_id('DBName')If you have a host with multiple IP address on it, and you need to change witch IP address it present it with on the Internet, you can change the Default IP address, by changing the source IP address on the default route
ip route change default via 192.168.0.254 src 192.168.0.10Of course the Linux host need to listen on the IP address.
You can see the changes by this command
ip route listdefault via 192.168.0.254 dev eth0 src 192.168.0.10Today i have a customer that got an Bad Request Error 400, when he try to logon to ADFS from inside their own network, with domain connected computers.
The error is only showing up in Internet Explorer, witch lead me to it might be a kerberos thing.
The service account that run the ADFS services, is “ita_service_admin”.
So looking at that account with setspn i can see witch SPN is register to ita_service_admin account.
setspn -l XXX\ita_service_adminThe where no SPN for the account. The ADFS url is: https://fs.YYY.dk so i added the following SPN to ita_service_Admin account:
setspn -S HOST/FS.YYY.DK XXX\ITA_SERVICE_ADMIN
setspn -S HTTP/FS.YYY.DK XXX\ITA_SERVICE_ADMINBut I got an error saying that HOST/FS.YYY.DK already exist. So i look for the SPN in the domain
This Code, will show all SPN in use in you Active Directory
cls
$search = New-Object DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher([ADSI]“”)
$search.filter = “(servicePrincipalName=*)”
$results = $search.Findall()
#list results
foreach($result in $results)
{
$userEntry = $result.GetDirectoryEntry()
Write-host “Object Name = “ $userEntry.name -backgroundcolor “yellow” -foregroundcolor “black”
Write-host “DN = “ $userEntry.distinguishedName
Write-host “Object Cat. = “ $userEntry.objectCategory
Write-host “servicePrincipalNames” $i=1
foreach($SPN in $userEntry.servicePrincipalName)
{
Write-host “SPN(“ $i “) = “ $SPN $i+=1
}
Write-host “”
}Find the SPN, and delete it from the account, i find the account under Administrator, so it looks like someone have change the service account for ADFS service from Administrator to ITA_SERVICE_ADMIN account in the past, without moving the SPN.
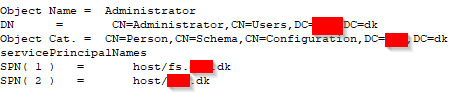
So delete the SPN from administrator account
setspn -D HOST/FS.YYY.DK XXX\administratorThen try to add it again to ITA_Service_Admin account.
setspn -S HOST/FS.YYY.DK XXX\ITA_SERVICE_ADMINRestart the ADFS service, and the ADFS is working again also from Internet Explorer.
How fast is data leving the cache, when it not access again.
With this query, you can see how fast data will get expire, and overwritten by new data in the cache.
SELECT @@servername AS INSTANCE
,[object_name]
,[counter_name]
, UPTIME_MIN = CASE WHEN[counter_name]= 'Page life expectancy'
THEN (SELECT DATEDIFF(MI, MAX(login_time),GETDATE())
FROM master.sys.sysprocesses
WHERE cmd='LAZY WRITER')
ELSE ''
END
, [cntr_value] AS PLE_SECS
,[cntr_value]/ 60 AS PLE_MINS
,[cntr_value]/ 3600 AS PLE_HOURS
,[cntr_value]/ 86400 AS PLE_DAYS
FROM sys.dm_os_performance_counters
WHERE [object_name] LIKE '%Manager%'
AND[counter_name] = 'Page life expectancy'Witch the query you can see how long time data will be in the cache/buffer.
With this query, you can see whitch database that is using most memory
SELECT COUNT(*) AS cached_pages_count ,
( COUNT(*) * 8.0 ) / 1024 AS MB ,
CASE database_id
WHEN 32767 THEN 'ResourceDb'
ELSE DB_NAME(database_id)
END AS Database_name
FROM sys.dm_os_buffer_descriptors
GROUP BY database_id
Whit this code, you can see how much of query in percent at this moment is reading from the cache/buffer.
DECLARE @value numeric(25, 2), @basevalue numeric(25, 2)
declare @Cachehitratio real
set @Cachehitratio = null
--Cache hit ratio
SELECT @value = cntr_value FROM master..sysperfinfo (nolock)
WHERE counter_name = 'Buffer cache hit ratio'
SELECT @basevalue = cntr_value FROM master..sysperfinfo (nolock)
WHERE counter_name = 'Buffer cache hit ratio base'
set @Cachehitratio= (@value / @basevalue) *100
select @Cachehitratio